Introduction
End tidal CO₂ range is a vital measurement in medical monitoring that indicates the amount of carbon dioxide (CO₂) at the end of an exhaled breath. This value helps healthcare professionals assess ventilation status, respiratory function, and metabolic activity. Understanding the normal range and variations is crucial in clinical settings such as anesthesia, intensive care, and emergency medicine. This article explains the importance of End Tidal CO₂ range, how to interpret it, and its role in patient care.
What is End Tidal CO₂?
End tidal CO₂ (ETCO₂) is the partial pressure or concentration of carbon dioxide released at the end of expiration. It is measured using capnography, a non-invasive technique that provides real-time information about ventilation, perfusion, and metabolism. ETCO₂ values are expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or as a percentage.
Normal End Tidal CO₂ Range
The typical End Tidal CO₂ range for a healthy adult is between 35 and 45 mmHg. Values outside this range may indicate respiratory or metabolic problems. For example, a low ETCO₂ level might suggest hyperventilation, whereas a high ETCO₂ level could indicate hypoventilation or impaired gas exchange.
Clinical Significance of End Tidal CO₂ Range
Monitoring ETCO₂ allows healthcare providers to evaluate ventilation efficiency and detect respiratory issues early. It is especially useful during anesthesia to ensure proper ventilation, in critical care to monitor patients on ventilators, and in emergency situations like cardiac arrest for confirming airway placement and assessing circulation.
Factors Affecting End Tidal CO₂ Range
Several factors influence the End Tidal CO₂ range including:
-
Ventilation rate and depth
-
Metabolic rate
-
Cardiac output
-
Pulmonary perfusion
-
Airway obstruction
Understanding these factors helps clinicians interpret ETCO₂ readings accurately.
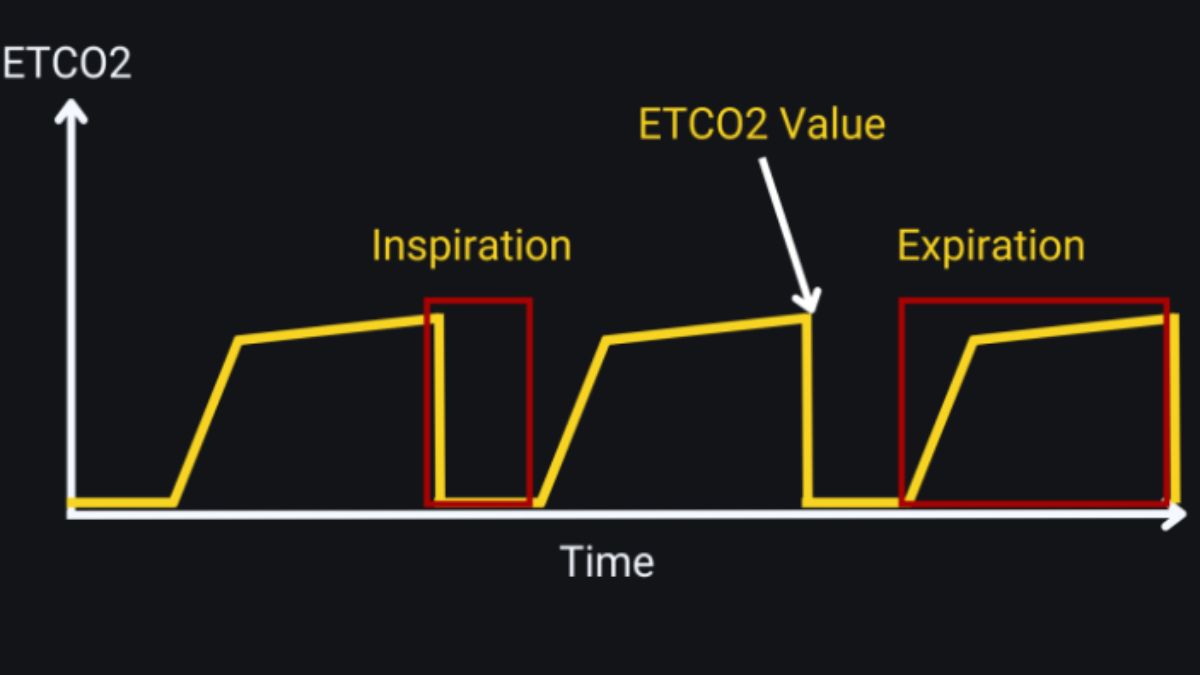
Capnography Waveforms and Interpretation
Capnography displays ETCO₂ levels as waveforms, providing visual insight into respiratory status. The shape and phases of the waveform can reveal airway obstructions, apnea, or other respiratory conditions. Recognizing abnormal waveforms is critical for timely intervention.
Differences Between End Tidal CO₂ and Arterial CO₂
While ETCO₂ provides an indirect measure of arterial CO₂ (PaCO₂), they are not always identical. The gradient between ETCO₂ and PaCO₂ depends on factors such as lung disease and ventilation-perfusion mismatch. Clinicians must understand these differences for precise patient assessment.
Applications of End Tidal CO₂ Monitoring
End Tidal CO₂ monitoring is used in:
-
Operating rooms during anesthesia
-
Intensive care units for ventilated patients
-
Emergency departments for airway management
-
Transport of critically ill patients
-
Sleep studies and pulmonary function testing
Each application benefits from accurate interpretation of ETCO₂ values.
Limitations of End Tidal CO₂ Monitoring
Though valuable, ETCO₂ monitoring has limitations. Conditions such as severe lung disease, low cardiac output, or equipment malfunction can affect accuracy. ETCO₂ should be interpreted alongside clinical findings and other monitoring tools.
Best Practices for Using End Tidal CO₂ Monitoring
To optimize ETCO₂ use:
-
Calibrate equipment regularly
-
Train staff in waveform interpretation
-
Combine ETCO₂ data with clinical context
-
Use in conjunction with other vital signs
Adhering to these practices enhances patient safety and monitoring efficacy.
Conclusion
Understanding the End Tidal CO₂ range is essential for healthcare professionals involved in patient respiratory monitoring. By recognizing normal and abnormal values and interpreting capnography waveforms, clinicians can make informed decisions that improve patient outcomes. Continuous education and proper equipment use are keys to effective ETCO₂ monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the normal End Tidal CO₂ range?
The typical range is 35 to 45 mmHg for healthy adults.
Why is ETCO₂ monitoring important?
It provides real-time information about ventilation and metabolism, helping detect respiratory issues early.
Can ETCO₂ values differ from arterial CO₂?
Yes, due to physiological factors, ETCO₂ is usually slightly lower than arterial CO₂.
What affects End Tidal CO₂ readings?
Ventilation, metabolism, cardiac output, and airway conditions all influence ETCO₂.
Is capnography useful in emergency settings?
Yes, it helps confirm airway placement and assess circulation during resuscitation.
What are common causes of low ETCO₂?
Hyperventilation, decreased cardiac output, or pulmonary embolism can lower ETCO₂.
Can ETCO₂ be used during sedation?
Yes, it helps monitor ventilation in sedated patients to prevent hypoventilation.
How often should ETCO₂ equipment be checked?
Regular calibration and maintenance ensure accurate readings and patient safety.